The keto diet, known for its high-fat, low-carbohydrate approach, has shown promise in managing neurological conditions, including dystonia. Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, leading to repetitive movements or abnormal postures. While traditional treatments include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery, emerging research suggests that dietary interventions, like the ketogenic diet, may offer additional benefits for managing symptoms of dystonia.
The ketogenic diet shifts the body’s primary energy source from carbohydrates to fats, leading to the production of ketones, which many believe have neuroprotective effects. This dietary approach has been widely studied in epilepsy and other neurological conditions, showing potential benefits due to its ability to stabilize neural activity and reduce inflammation. In this guide, we will explore the potential effects of the keto diet on dystonia, examining the science behind it, the potential benefits and risks, and practical considerations for those considering this diet as a complementary approach to managing dystonia.
1. Understanding Dystonia: Symptoms and Causes
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder that causes involuntary muscle contractions, leading to repetitive movements or abnormal postures. It can affect a single part of the body (focal dystonia), multiple parts (segmental dystonia), or the entire body (generalized dystonia). The symptoms can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
- Causes of Dystonia: The exact cause of dystonia is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve abnormal functioning in the basal ganglia, the part of the brain responsible for coordinating movement. Dystonia can be genetic or acquired due to factors such as brain injury, stroke, infections, or as a side effect of certain medications.
- Current Treatments: Traditional treatments for dystonia include medications that target neurotransmitter activity, such as anticholinergics, muscle relaxants, and botulinum toxin injections. Physical and occupational therapy can also help manage symptoms, and in severe cases, deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery may be considered.
2. What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates for energy. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the body enters a state of ketosis, where it produces ketones from fat to use as an alternative energy source.
- How the Keto Diet Works: In a typical diet, the body converts carbohydrates into glucose, which serves as the primary energy source. When you limit carb intake, the body starts breaking down fats into ketones, which it uses for energy, especially in the brain. This metabolic state is known as ketosis.
- Common Foods on a Keto Diet: The keto diet emphasizes foods that are high in fats, moderate in protein, and very low in carbohydrates. Common foods include meats, fatty fish, eggs, butter, oils, nuts, seeds, and non-starchy vegetables. Foods to avoid include grains, sugars, fruits, and starchy vegetables.
3. How the Keto Diet May Affect Dystonia
Research suggests that the ketogenic diet may have neuroprotective effects that could benefit individuals with dystonia. Although the direct impact of the keto diet on dystonia is still under investigation, several mechanisms could explain its potential benefits.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Ketones produced during ketosis provide a more stable and efficient energy source for the brain. This shift in metabolism may help reduce abnormal neural firing and improve motor control, potentially alleviating some dystonia symptoms.
- Reduction in Inflammation: The keto diet has been shown to reduce systemic inflammation, which is believed to play a role in various neurological disorders. By reducing inflammation, the keto diet may help alleviate some of the neurological dysfunctions associated with dystonia.
- Improved Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within cells, play a role in dystonia when they become dysfunctional. The ketogenic diet enhances mitochondrial function, potentially contributing to improved neural health and better symptom management for dystonia patients.
4. Potential Benefits of the Keto Diet for Dystonia Patients
While more research is needed, some potential benefits of the keto diet for dystonia patients include symptom reduction and improved quality of life. Early evidence and anecdotal reports suggest that the ketogenic diet could help manage some aspects of dystonia by providing a stable energy source for the brain and reducing excitability.
- Symptom Management: Some individuals with dystonia report a reduction in muscle spasms and improved motor control when following a ketogenic diet. The exact reasons for these improvements are still being studied, but they are thought to relate to the diet’s effects on brain metabolism and inflammation.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Studies associate the keto diet with improved cognitive function, which may benefit dystonia patients experiencing cognitive difficulties as part of their condition. The brain uses ketones as an energy source, which supports better mental clarity and focus.
- Reduced Medication Dependence: The ketogenic diet may help some individuals reduce their medication use, offering benefits given the side effects that often accompany many dystonia medications. However, it’s important to make any changes to medication under medical supervision.
5. Risks and Considerations of the Keto Diet for Dystonia
While the ketogenic diet may offer benefits, it also comes with potential risks and considerations, particularly for those with dystonia. It’s important to approach this dietary change carefully and under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
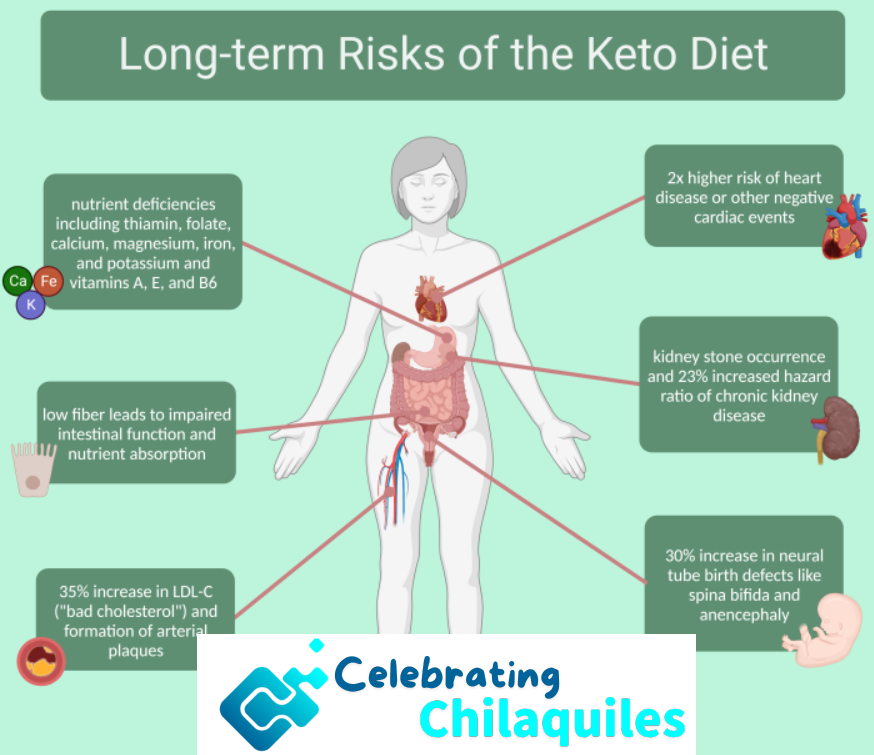
- Nutritional Deficiencies: The restrictive nature of the keto diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies, particularly in fiber, vitamins, and minerals typically found in carbohydrate-rich foods. It’s important to monitor nutrient intake and consider supplements if necessary.
- Initial Side Effects: The transition into ketosis can cause temporary side effects, often referred to as the “keto flu.” Symptoms may include fatigue, headache, nausea, and irritability. These usually subside within a few days as the body adjusts to ketosis.
- Not Suitable for Everyone: Healthcare professionals generally do not recommend the keto diet for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as pancreatitis, liver disease, or disorders of fat metabolism. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting the diet to ensure it is safe for your specific health needs.
6. How to Start a Keto Diet Safely for Dystonia Management
If you’re considering the keto diet as a complementary approach to managing dystonia, it’s important to start safely and strategically. Here are some steps to help you begin.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before starting the keto diet, consult with a neurologist or a dietitian familiar with ketogenic therapies. They can help tailor the diet to your specific health needs and monitor your progress.
- Gradual Transition: To reduce the risk of side effects, consider gradually reducing carbohydrates over a week or two instead of making an abrupt change. This allows your body to adjust more comfortably to the new fuel source.
- Monitor Your Health: Regularly monitor your health and symptoms once you start the keto diet. Keep track of how your dystonia symptoms respond, and make adjustments to the diet as needed with professional guidance.
7. FAQs: Keto Diet for Dystonia
Can the Keto Diet Cure Dystonia?
No, the keto diet is not a cure for dystonia. However, it may help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for some individuals when used alongside traditional treatments.
How Long Does It Take to See Results from the Keto Diet for Dystonia?
The time frame for seeing results can vary. Some people may notice improvements in symptoms within a few weeks, while others may take longer. Consistency and adherence to the diet are key factors.
Are There Any Risks of Worsening Dystonia Symptoms on the Keto Diet?
While many find benefits, there is a possibility that the keto diet may not work for everyone, and in rare cases, it could potentially exacerbate symptoms. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to monitor any changes.
What Foods Should Be Avoided on the Keto Diet?
On the keto diet, avoid high-carb foods like grains, sugars, fruits (except small amounts of berries), starchy vegetables, and processed foods. Focus on high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carb food choices.
Can Children with Dystonia Follow a Keto Diet?
Children with neurological conditions can follow the keto diet under strict medical supervision. It’s crucial to collaborate with a healthcare provider to ensure the diet meets nutritional needs and remains safe for the child
Conclusion: Keto Diet for Dystonia
The keto diet offers a promising complementary approach for managing dystonia, with potential benefits including reduced symptoms and enhanced quality of life. While it’s not a cure, its neuroprotective properties and ability to stabilize brain function make it an option worth exploring under professional guidance. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making dietary changes, especially when dealing with complex neurological conditions like dystonia. By taking a careful and informed approach, you can determine if the ketogenic diet is a suitable addition to your dystonia management plan.